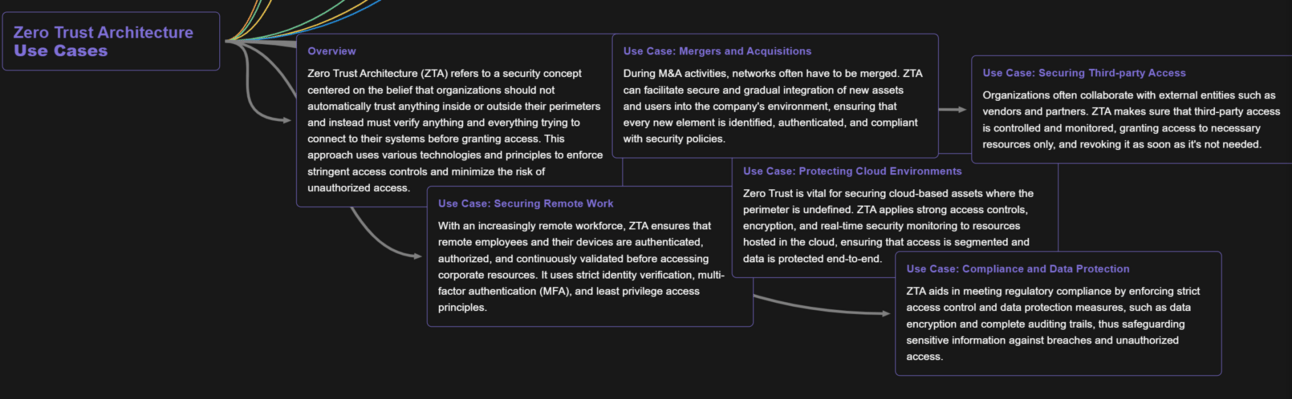
As a member of the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), I've worked on developing content related to Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) and its principles. Recently, we've been discussing the importance of real-world use cases in fully understanding ZTA's concepts and implementation strategies. To help with this, I've created a mind map that breaks down the key components of ZTA and applies them to practical scenarios. Check it out to gain a better understanding of how ZTA can be applied in the real world. #ZeroTrustArchitecture #CloudSecurityAlliance #Cybersecurity #RealWorldUseCases

Cloud with Zero Trust with Initial Planning
Leveraging Zero Trust Architecture for Enhanced Security: A Practical Guide
In the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has emerged as a transformative approach, shifting away from traditional perimeter-based security to a continuous verification model. By adopting ZTA, organizations can effectively protect their sensitive data and critical assets from evolving cyber threats. To effectively implement ZTA, it's crucial to understand its real-world applications and adopt a structured implementation approach.
Harnessing ZTA for Real-world Scenarios
ZTA's versatility extends to various scenarios, enabling organizations to safeguard their critical assets and data:
1. Cloud Platform Security:
Establish a ZTA gateway to control and manage cloud access, ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data.
Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all root accounts, enhancing authentication and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Utilize SAML authorization for seamless integration with SaaS or PaaS applications, streamlining access and enhancing security.
2. Managing Staff Access:
Protect root accounts with MFA, safeguarding these highly sensitive access points.
Implement ZTA-based access policies to restrict access based on authorized roles and permissions.
Conceal sensitive data and resources behind policies to minimize their visibility and exposure to potential threats.
Limit public visibility of sensitive data and resources to reduce the attack surface and enhance overall security posture.
3. Remote Access for Third-party Partners:
Employ ZTA policies to authenticate and authorize third-party users and devices, ensuring that only trusted entities can access critical resources.
Grant access at the granular level required for specific tasks, preventing lateral movement and unauthorized data access.
Mitigate supply chain risk by minimizing the attack surface and ensuring that only authorized third parties have access to critical systems.

A Structured Approach for ZTA Implementation
Effective ZTA implementation requires a structured plan that aligns with the organization's unique needs and security requirements:
1. Identify Critical Protection Surface:
Assess data and asset criticality to prioritize protection efforts.
Map the protection surface, encompassing data, assets, processes, and access controls.
Determine one or more protection areas based on organizational priorities.
2. Expand and Prioritize Protection Surface:
Define a rollout strategy for implementing ZTA across the remaining protection surface.
Develop a business case to justify resource allocation and investment in ZTA implementation.
Establish clear criteria for prioritizing use cases and implementation timelines.
3. ZTA Planning Steps:
Understand the Protect Surface:
Create a comprehensive inventory of data, assets, and their configurations.
Utilize asset discovery tools and IDS to gather asset information automatically.
Develop a CMDB (Configuration Management Database) for asset tracking and management.
Identify Data Locations and Data Hosting:
Determine where sensitive data resides and how it is accessed.
Identify potential vulnerabilities and data leakage paths through data flow analysis.
Implement data classification and protection mechanisms to safeguard sensitive data.
Identify Services and Processes:
Map critical services and business processes that require protection.
Assess the potential impact of service disruptions or unauthorized access.
Implement ZTA policies to safeguard critical services.
Prioritize Entities and Discovery:
Prioritize entities, such as users, devices, and applications, based on their access requirements.
Utilize discovery tools to identify and classify assets.
Implement access control mechanisms based on risk assessment and classification.
Harnessing ZTA for a Secure Future
By adopting real-world use cases and implementing ZTA with a structured approach, organizations can effectively enhance their overall security posture, safeguard sensitive data, and mitigate cybersecurity risks. Remember, ZTA is an ongoing journey, not a one-time project, and continuous adaptation and improvement are essential to maintain a strong defense against evolving threats.
Image link for better view https://files.mymap.ai/exports/bIbgvjbtnhHpF/KPNCilVCcCKFMYpK_RygL.png